Introduction
What is a Payment Gateway?
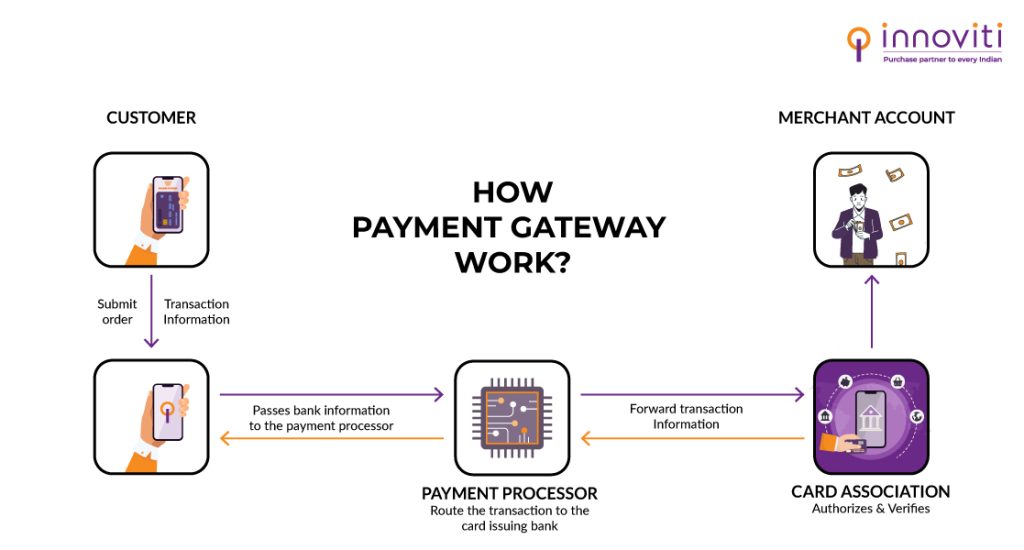
A payment gateway is software that processes payments online. It is used only for online transactions and offers limited payment options. In India, many banks, such as Axis Bank, HDFC, and Union Bank of India, serve as payment gateways.
What is a Payment Aggregator?
Difference Between Payment Aggregator and Payment Gateway

Advantages of Payment Aggregators for Businesses
Quick Setup:
Easy Integration:
Reduced Compliance Burden:
Aggregated Merchant Accounts:
Faster Onboarding:
Cost-Effective for Small Businesses:
Access to Multiple Payment Methods:
Unified Dashboard:
Risk Management:
Payment aggregators often include built-in risk management tools to help identify and mitigate fraud. This added layer of security can be beneficial for businesses concerned about online payment risks.
Scalability:
Payment Aggregator vs Payment Gateway
| Basis of Distinction | Payment Aggregator | Payment Gateway |
|---|---|---|
| Scope | Online/Offline transactions | Only online transactions |
| Primary Function | Acts as an interface | Acts as intermediary |
| Multiple Payment Options | Yes | No, limited payment options |
| Owned By | Generally, ownership lies with fintech companies and financial service providers | Banks, vendors, payment aggregators, etc. |
| Authorization | Payment Card Industry – Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) certification | RBI authorization under PSSA is required |
| Examples | Innoviti, Bill Desk, PayUMoney, etc. | HDFC, ICICI, Axis banks, Razorpay, etc. |
| Integrated Solution | Full integration is available here | Relatively less integration compared to aggregators |
Conclusion
Frequently Asked Questions
There are three types of payment gateways such as
- Hosted Payment Gateways
- Self-Hosted or Pro-Hosted Payment Gateways
- API Hosted Payment Gateways
Before choosing the right payment gateway for your business, think about important factors like security, compliance with rules, data analytics, and how easily it can be integrated into your system. Picking the right gateway helps your business grow and keeps your customers happy.
For offering the payment gateway processing services, your service provider charges a fee. The different components of payment gateway charges comprise initial setup charges, yearly maintenance charges, MDR, integration charges for your online website and gateway integration, etc.
