Compliance And Beyond: Ensuring A Smooth Payment Authorization Process For Merchants
Payment or card authorization is an integral part of every online transaction and digital payment process.
Apart from acknowledging that a cardholder has the funds available to complete a particular purchase, it is a crucial security step that provides card issuers and merchants a regular way to keep a tab on potentially unauthorized transactions.
Understanding the basics involved in a payment authorization process can go a long way in enhancing customer experience and managing businesses with great ease for merchants.
What is Payment Authorization?
In other words, payment authorization enables merchants to confirm with card issuers or banks that their customers have enough credit or money to cover the cost of the transaction.
How does card authorization work?
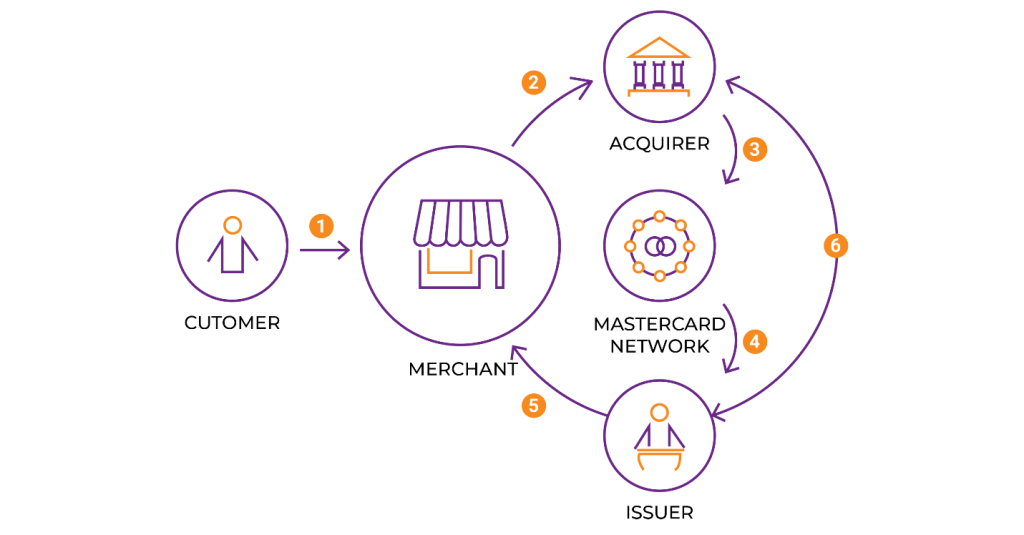
Here's a snapshot of how the card authorization process unfolds:
- The customer purchases goods or services by swiping, inserting, or tapping their card at the point-of-sale (POS) terminal or card reader or by entering their credit or debit card details online, referred to as a card-not-present (CNP) transaction.
- The merchant’s payment processor then sends an authorization request to the acquiring bank, using a card network (Visa or Mastercard).
- The acquiring bank captures the transaction’s relevant information, including the purchase amount, the card number, and the merchant’s details.
- The acquiring bank then routes it back via the card network, which forwards the authorization request to the issuing bank.
- The issuing bank then checks for three things: the card is valid and in use, evaluates the transaction for potential fraud, and checks the availability of sufficient funds or credit available to cover the amount being requested for approval.
- The issuing bank then sends an authorization code back to the card network through the same channels.
- If the authorization is approved, the transaction is successfully processed. If it’s declined, the transaction is cancelled and a denial code is received providing the relevant details about why the card authorization failed, which may be due to insufficient funds, an unauthorized transaction, or a technical glitch.
Types of Payment Authorization Methods
Credit or debit card authorization: As one of the most common payment authorization methods, it involves verifying the card details of a customer, such as the credit or debit card number, expiration date, and security code.
Automated Clearing House (ACH) authorization: By this method, businesses can accept payments directly from a customer’s bank account.
E-wallet (electronic wallet) authorization: An e-wallet is a digital wallet that stores a customer’s payment information, such as card details and bank account details.
Token-based authorization: This involves replacing a customer’s sensitive payment data with a unique identifier or token, which is used to process the payment. A customer’s payment information is stored securely by payment gateways.
Biometric authorization: This is a mode of security that uses a customer’s biometric data, such as fingerprints, and facial or voice recognition to verify their identity and authorize a payment.
The Role of Payment Gateways in Authorization
Authentication and verification: This involves checking the validity of a card number, expiration date, and security code using advanced algorithms and tools to identify any potential fraudulent activity or unauthorized transactions. Additionally, payment gateways also carry out address verification checks of a customer.
Encryption and security: Payment gateways employ advanced encryption technologies to protect sensitive payment details such as card numbers, expiry dates, and security codes. While complying with security standards such as the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS), payment gateways ensure every transaction is securely initiated.
Integration and customization: Payment gateways can seamlessly integrate with a merchant’s website or an e-commerce platform. A wide range of customization options include customizing a payment page and checkout process.
Multiple payment options: Payment gateways offer multiple payment avenues which can help merchants cater to a wider target audience.
Why is payment authorization necessary?

Payment authorization is necessary for various parties, including customers, banks or card issuers, and merchants for the following reasons:
Checking frauds: Payment authorization is needed to verify the authenticity of every transaction and save a customer from potential fraud.
Enhancing security: Payment authorization is a meticulous validation process that ensures that a particular transaction is legitimate.
Minimalizing chargebacks: The process of chargebacks can be a time-consuming and expensive exercise for a merchant. Payment authorization minimizes the chances of chargebacks by validating transactions before they are processed.
What happens if the payment authorization Fails?
At the time of the payment authorization process, the issuing bank may recognize the card as either lost, stolen, frozen or past its expiration date. There is also a possibility that the transaction itself may be deemed as a suspicious and potentially unauthorized transaction. As a result, the transaction gets rejected, and a check for suspicious charge activity is likely to occur.
Technical glitches could also lead to payment authorization failure. Usually, this occurs when issues with configuration or online submission disrupt the information being supplied to the processor. An error code gets generated, and the sale process remains incomplete.
A merchant should avoid completing the transaction until they receive proper authorization at such a time. Online businesses should also avoid shipping any products until the issue gets resolved.
Usually, a merchant will need to fix a technical glitch that arises from payment authorization failure. There is a likelihood that a buyer may be having issues with their cards or device, and will need to resolve the problems at their end.
How to improve payment authorization rates?
By optimizing payment processes, a merchant can ensure more successful transactions. This in turn can lead to higher revenue.
Enable tokenization technology: Tokenization turns a customer’s sensitive payment data into tokens. This alternative makes it much more difficult for a fraudulent person to access or steal a customer’s real data.
Use payment authentication: 3D Secure (3DS) is a payment security protocol that provides an extra layer of security in online card transactions.
Leverage emerging technologies: Choose a fraud detection solution with advanced features like machine learning (ML), artificial intelligence (AI), and real-time data analysis that will only decline payments depending on current threats.
Utilize checkout data Collecting important billing information during the checkout process could influence payment authorization rates. Through a collection of additional billing information, a merchant can share more comprehensive and detailed data on every transaction with the issuing banks, which is more likely to verify the payment as legitimate.
Best Practices for Payment Authorization
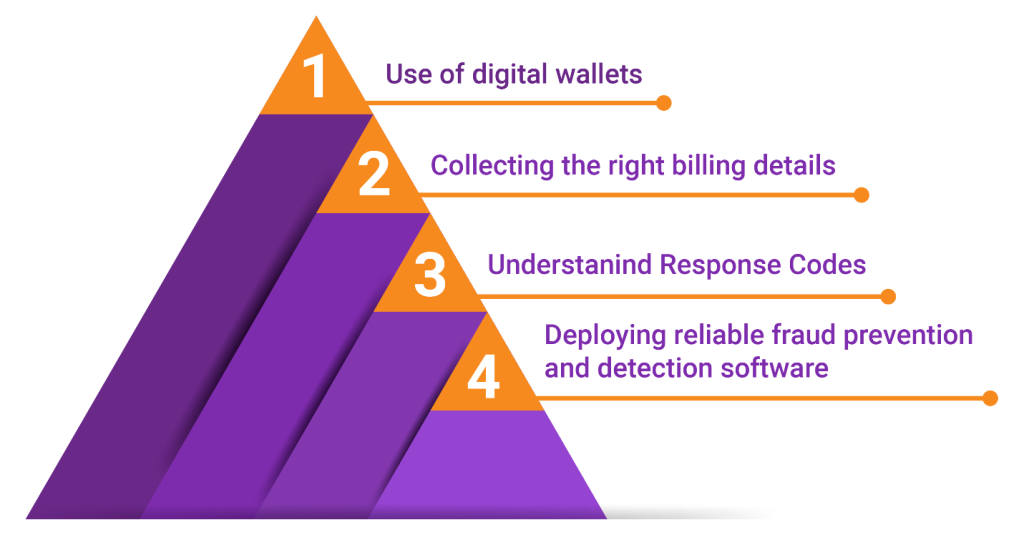
Use of digital wallets: Digital wallets are to be preferred as these rely on factors such as biometric verification to secure a transaction, they tend to register higher rates of acceptance than any of the alternative payment methods.
Collecting the right billing details: It must be ensured that a customer submits their name, card number, card verification value (CVV) number, and billing address at the checkout.
Understanding response codes: Understanding and regularly reviewing card authorization numbers and denial codes, a merchant can identify transaction patterns is crucial. This way, they can understand why authorization requests are witnessing an uptick or dip.
Deploying reliable fraud prevention and detection software: Embedding anti-fraud tools not only offers an added layer of security to each transaction but also builds a reputation as a trustworthy merchant, thus influencing payment authorization in the bargain.
Conclusion
Considering the recent surge in online transactions, payment authorization, also referred to as pre-authorization or card authorization, is the first step in the payment process. During the payment authorization process, funds are usually held and not credited.
While the payment authorization hold may lead to an increase in the time that merchants can access the funds, it aids in reducing financial liability and takes care of chargeback fraud.
Merchants can optimise their payment authorization processes by deploying advanced fraud prevention measures, ensuring the accuracy of customer information, and employing payment gateways and processors that provide better success rates. Regular updating of payment systems and remaining up-to-date about industry best practices can go a long way in reducing failed authorizations.
Overall, payment authorizations work together with cybersecurity technologies to boost the security of online transactions. With the evolution of technology, payment authorization will experience a parallel enhancement and is expected to offer more security, efficiency, and convenience for all parties involved.
